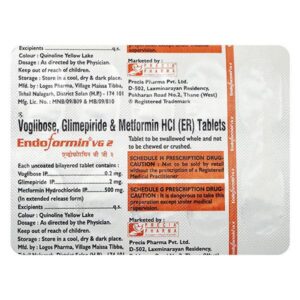
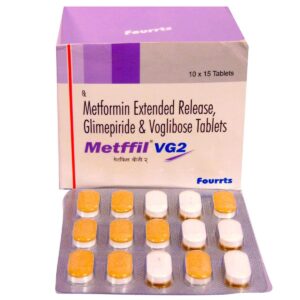
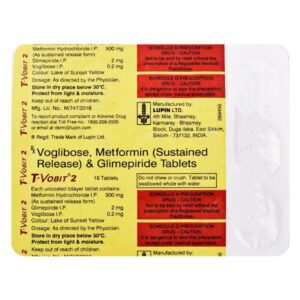
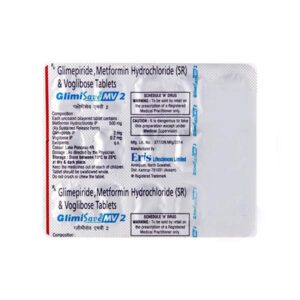
GLIMEPIRIDE + METFORMIN + VOGLIBOSE
Glimepiride: Glimepiride is an oral medication used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus. It belongs to the class of medications called sulfonylureas, which work by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas and increasing the sensitivity of tissues to insulin. This helps to lower blood sugar levels.
The recommended dose of glimepiride varies depending on individual patient factors such as age, kidney function, and response to treatment. Generally, the starting dose is 1-2 mg taken orally once daily with breakfast or the first main meal of the day. The dose may be adjusted by the healthcare provider based on blood sugar control.
As with most medications, glimepiride may cause side effects. Common side effects include dizziness, headache, nausea, and low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Hypoglycemia symptoms include excessive sweating, shaking, dizziness, blurred vision, and confusion. It is important to monitor blood sugar levels regularly and be aware of the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia.
In rare cases, glimepiride can cause more serious side effects such as allergic reactions, liver problems, and blood disorders. Thus, it is crucial to contact a healthcare professional if any unusual symptoms occur after starting glimepiride.
It is important to note that glimepiride should be taken as directed by a healthcare provider and should not be used for the treatment of type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis. The medication is usually prescribed as part of a comprehensive treatment plan including lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise.
This information is not exhaustive, and it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or read the medication guide for more detailed instructions and precautions before taking glimepiride.
Metformin: Metformin is an oral medication commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is an antidiabetic drug belonging to the biguanide class. Metformin works by lowering glucose production in the liver and improving the body’s response to insulin, resulting in better control of blood sugar levels.
The drug is usually taken in tablet form, and the usual starting dose is 500 mg or 850 mg once or twice a day, with meals. The dose may be gradually increased by the healthcare provider based on individual needs, up to a maximum daily dose of 2,550 mg.
Metformin is primarily used to control blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes, either alone or in combination with other antidiabetic medications like insulin or sulfonylureas. It may also be prescribed for the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition characterized by hormonal imbalance and insulin resistance.
As with any medication, metformin can cause side effects. The most common side effects include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach upset. These side effects are usually temporary and may improve over time. Taking the medication with meals can help minimize these symptoms. Other less common side effects may include metallic taste in the mouth, weakness, muscle pain, and sometimes low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia). Lactic acidosis, a rare but serious complication, may occur in individuals with underlying kidney or liver problems, or in cases of overdose.
It is important to inform your healthcare provider about any other medications you are taking, as some drugs, such as certain antibiotics or contrast dyes used in imaging tests, may interact with metformin and increase the risk of lactic acidosis.
Overall, metformin is a widely prescribed medication for the management of type 2 diabetes and may be an effective option for individuals with diabetes or PCOS. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dose and to monitor for any potential side effects or interactions.
Voglibose: Voglibose is an oral anti-diabetic drug that is used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus. It belongs to a class of medications called alpha-glucosidase inhibitors.
The main mechanism of action of Voglibose is to slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, primarily in the small intestine. It achieves this by inhibiting the alpha-glucosidase enzyme, which breaks down complex sugars and starches into simpler sugars that can be absorbed by the body. By delaying the absorption of carbohydrates, voglibose helps in reducing the increase in blood sugar levels after a meal.
The usual recommended dose of Voglibose is 0.2-0.3 mg, taken three times daily before meals. The dose may be adjusted based on individual response and blood sugar levels.
Like any medication, Voglibose can cause side effects. Common side effects include abdominal discomfort, bloating, flatulence (gas), and diarrhea. These gastrointestinal side effects usually resolve on their own as the body adjusts to the medication. Rarely, Voglibose may also cause hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), but this is more likely to occur when taken in combination with other diabetes medications that can lower blood sugar.
It is important to note that Voglibose should not be used in individuals with a known allergy to the drug or any of its components. Additionally, it may not be suitable for patients with certain medical conditions, such as conditions affecting the kidneys or liver. Therefore, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before starting Voglibose or making any changes to diabetes treatment.