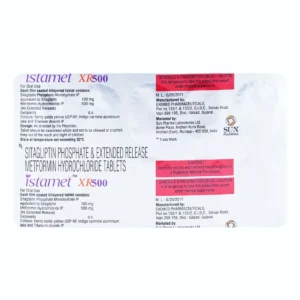
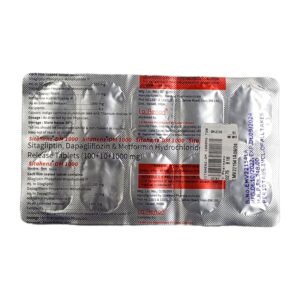
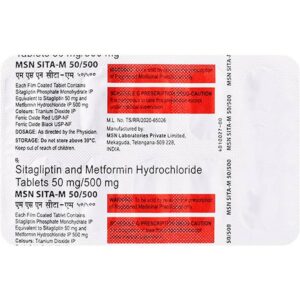
METFORMIN + SITAGLIPTIN PHOSPHATE
Metformin: Metformin is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It works by decreasing the amount of glucose produced by the liver and improving the body’s response to insulin, a hormone that helps control blood sugar levels.
The recommended starting dose of metformin is generally 500 mg or 850 mg, taken orally once or twice a day with meals. The dosage may be increased gradually based on blood sugar levels, but the maximum daily dose should not exceed 2,550 mg.
Common side effects of metformin include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. These side effects are usually mild and resolve on their own. In some cases, metformin can also cause a metallic taste in the mouth or a decrease in vitamin B12 levels.
Rare but more serious side effects can occur, such as lactic acidosis, a potentially life-threatening condition. Lactic acidosis is most likely to occur in people with kidney or liver problems, congestive heart failure, or severe infections. It is important to seek immediate medical attention if symptoms such as muscle pain, shortness of breath, or unusual tiredness occur.
Metformin is generally well-tolerated and considered safe for most people, but it may not be suitable for everyone. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting or changing any medication regimen.
Sitagliptin Phosphate: Sitagliptin phosphate is a medication commonly prescribed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. It is marketed under the brand name Januvia.
The primary use of Sitagliptin phosphate is to help control blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. It is often prescribed as an adjunct to diet and exercise when these lifestyle changes alone are not sufficient to manage blood sugar levels. It is not used for the treatment of type 1 diabetes.
The mechanism of action of Sitagliptin phosphate is through its inhibition of an enzyme called dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). DPP-4 is responsible for breaking down incretin hormones, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which play a role in regulating blood sugar levels. By inhibiting DPP-4, Sitagliptin phosphate increases the levels of active incretin hormones, leading to increased insulin secretion and decreased glucagon production. This ultimately results in improved blood sugar control.
The typical starting dose of Sitagliptin phosphate is 100 mg once daily, with or without food. The dosage may be adjusted based on individual response and tolerability. It is important to follow the instructions of the prescribing healthcare professional and not to modify the dosage without their guidance.
Like any medication, Sitagliptin phosphate may cause side effects. Common side effects can include upper respiratory tract infections, sore throat, headache, and diarrhea. In rare cases, it may also cause serious side effects such as pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) and severe allergic reactions. It is important to seek immediate medical attention if any signs of pancreatitis, such as severe abdominal pain or persistent nausea/vomiting, occur. Allergic reactions may present as rash, itching, swelling, dizziness, or difficulty breathing.
It is crucial to discuss any existing medical conditions or medications with a healthcare professional before starting Sitagliptin phosphate to ensure its safe use and compatibility with other treatments. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and follow-up appointments with a healthcare professional are typically required to assess the effectiveness and safety of Sitagliptin phosphate.